Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) and IRM
There are many business drivers and technology reasons for adopting data center infrastructure management (DCIM) and infrastructure Resource Management (IRM) techniques, tools and best practices. Today’s agile data centers need updated management systems, tools, and best practices that allow organizations to plan, run at a low-cost, and analyze for workflow improvement. After all, there is no such thing as an information recession driving the need to move process and store more data. With budget and other constraints, organizations need to be able to stretch available resources further while reducing costs including for physical space and energy consumption.
The business value proposition of DCIM and IRM includes:
- End to End (E2E) insight into IT resources (facilities, hardware, software, tools, people)
- Timely access to information about IT resources and inventory for decision making
- Metrics and measurements for service planning, budgeting, and compliance audits
- Enhance efficiency and productivity stretching available budgets further
- Agility and flexibility to adapt to changing business conditions
- Improve reliability, availability, serviceability (RAS) and Quality of Service (QoS)
- Eliminate islands or pockets of underutilized hardware and software resources
- Removing complexity and waste which results in cost savings
- Meet service level agreements (SLA) and service level objectives (SLO)
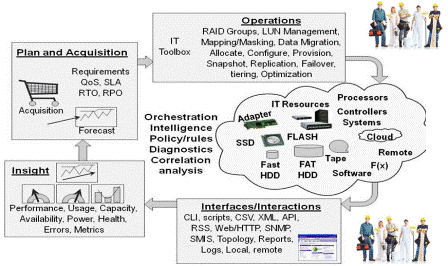
Data Center Infrastructure Management or DCIM also known as IRM has as their names describe a focus around management resources in the data center or information factory. IT resources include physical floor and cabinet space, power and cooling, networks and cabling, physical (and virtual) servers and storage, other hardware and software management tools. For some organizations, DCIM will have a more facilities oriented view focusing on physical floor space, power and cooling. Other organizations will have a converged view crossing hardware, software, facilities along with how those are used to effectively deliver information services in a cost-effective way.
Common to all DCIM and IRM practices are metrics and measurements along with other related information of available resources for gaining situational awareness. Situational awareness enables visibility into what resources exist, how they are configured and being used, by what applications, their performance, availability, capacity and economic effectiveness (PACE) to deliver a given level of service. In other words, DCIM enabled with metrics and measurements that matter allow you to avoid flying blind to make prompt and effective decisions.
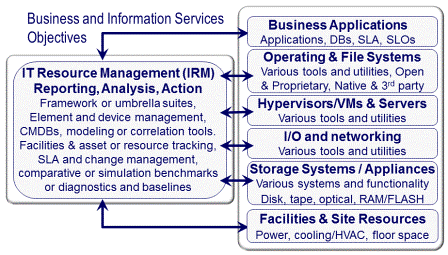
DCIM comprises the following:
- Facilities, power (primary and standby, distribution), cooling, floor space
- Resource planning, management, asset and resource tracking
- Hardware (servers, storage, networking)
- Software (virtualization, operating systems, applications, tools)
- People, processes, policies and best practices for management operations
- Metrics and measurements for analytics and insight (situational awareness)
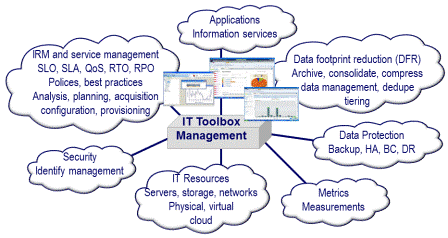
The evolving DCIM model is around elasticity, multi-tenant, scalability, flexibility, and is metered and service-oriented. Service-oriented, means a combination of being able to rapidly give new services while keeping customer experience and satisfaction in mind. Also part of being focused on the customer is to enable organizations to be competitive with outside service offerings while focusing on being more productive and economic efficient.
